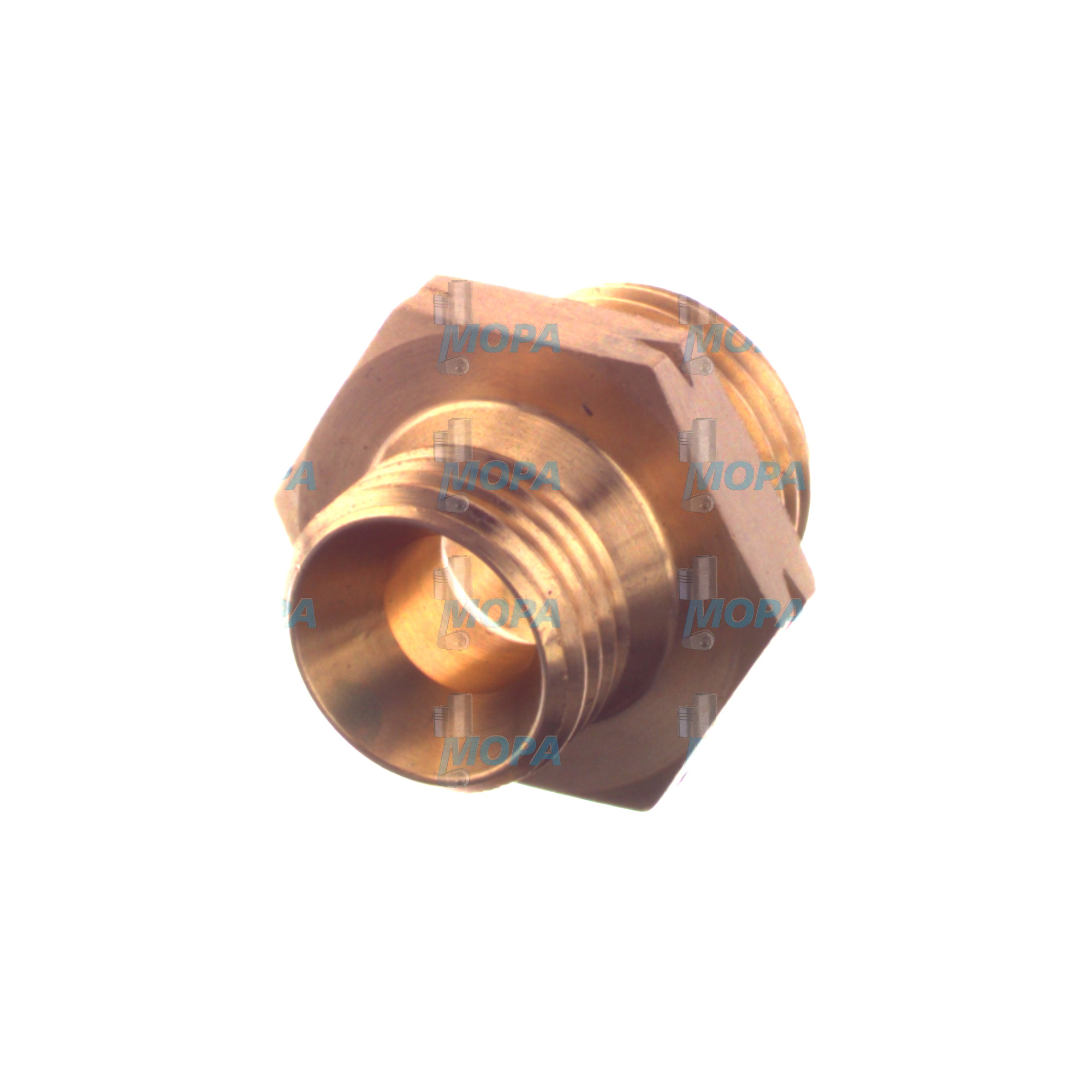
REDUCING UNION for Fittings and armatures in engine systems
Fittings and armatures form the connective tissue of an engine’s fluid and air networks. They link pipes, tubes, hoses, valves, and instruments across fuel oil, lube oil, coolant, hydraulics, and compressed air circuits. Within this category, a REDUCING UNION is a precise connector that joins lines of different diameters while maintaining a sealed, pressure-rated path. In marine engine and diesel engine environments—where vibration, thermal cycling, and corrosive atmospheres are daily reality—well-specified fittings and armatures safeguard flow reliability, prevent leaks, and protect performance-critical components.
From fuel conditioning skids to jacket water manifolds, the right connection strategy determines how efficiently media move, how easily systems are maintained, and how reliably the engine delivers power. Fittings and armatures provide modularity, serviceability, and compliance with engine-maker specifications. When integrated with a correctly sized REDUCING UNION, engineers can adapt legacy lines, upgrade components, or integrate instruments without compromising integrity or safety.
Technical function of Fittings and armatures and the role of a REDUCING UNION in marine engines
Technically, fittings and armatures enable leak-tight, mechanically stable transitions between components that often operate at high pressure and temperature. They manage directional changes (elbows), disconnections (unions), branching (tees), shut-off (valves), throttling (needle valves), and measurement (manifolds). A REDUCING UNION specifically couples two tubes or pipes of different diameters while preserving alignment, sealing geometry, and load distribution. In a marine engine, this is common when connecting a new sensor line to an existing main run, adapting to a revised injector feed, or retrofitting a filtration upgrade.
Depending on the system design, REDUCING UNION solutions may be compression/bite-type (DIN 2353/ISO 8434), flare/JIC (SAE J514), ORFS with O-ring face seal, or threaded (NPT, BSPP/BSPT). Materials are selected to match media and environment—316/316L stainless steel for corrosion resistance in seawater atmospheres, carbon steel for non-corrosive circuits, or copper-nickel where marine service dictates. Precision machining, correct surface finish, and controlled ferrule geometry ensure repeatable sealing. In diesel engine fuel systems, a REDUCING UNION minimizes turbulence at the diameter change, limiting pressure drop and protecting pump stability and injector performance.
Well-engineered fittings and armatures also mitigate vibration-induced loosening through appropriate seating angles, thread forms, and use of bite-type rings or O-ring face seals. They withstand thermal expansion by providing controlled flexibility at junction points. In measurement loops, they contribute to accurate readings by maintaining laminar flow upstream of sensors. In safety-relevant circuits—fuel, starting air, and hydraulics—the right connection strategy is essential to preventing atomized leaks and fire risk.
- · Leak-tight sealing under pressure and vibration
- · Compatible with diesel engine and marine engine media
- · Multiple standards: DIN 2353/ISO 8434, SAE J514, ORFS, NPT, BSPP/BSPT
- · Materials matched to service: 316/316L, carbon steel, CuNi, brass
- · Low pressure drop at transitions with the correct REDUCING UNION
- · Service-friendly modular unions and valves
- · Corrosion resistance for offshore and engine room environments
- · Traceable manufacturing and pressure testing from OEM parts suppliers
Why Fittings and armatures with the right REDUCING UNION are critical for engine operation
Reliability and service life of engines depend on the integrity of every connection. A worn tube nut, a deformed ferrule, or a misapplied REDUCING UNION can lead to weeping joints, sudden line failures, or progressive loss of pressure. The consequences range from reduced fuel efficiency and overheating to unplanned shutdowns and safety incidents. In high-pressure diesel fuel lines, even minor leakage compromises injection accuracy and combustion stability. In cooling circuits, poorly matched reductions induce cavitation and hotspots. On starting air manifolds, inadequate fittings can loosen under pulsation, risking blow-off and associated damage.
Correctly selected fittings and armatures maintain consistent flow, keep vibration loads under control, and ensure service crews can isolate, replace, and recommission components quickly. When a REDUCING UNION for marine engine instrumentation is dimensionally accurate and correctly rated, it allows clean integration of gauges and sensors without reworking primary lines—reducing downtime and error potential.
Advantages of OEM spare parts suitable for Fittings and armatures and every REDUCING UNION
Using OEM spare parts suitable for fittings and armatures delivers measurable benefits across performance, reliability, budget, and service life. The dimensional accuracy of threads, cones, and ferrules improves assembly repeatability and reduces the risk of galling or over-torque. Verified metallurgy and heat treatment provide predictable strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance, especially vital for a REDUCING UNION in diesel engine fuel or lube circuits. Pressure and vibration testing aligned with engine-maker requirements supports stable operation over long service intervals. Documentation and traceability streamline inspections and class approvals on board.
Procurement teams also benefit from consistent availability of matched subcomponents—nuts, sleeves, bodies, and seals—so maintenance crews can replace exactly what is needed. With OEM parts, the sealing system is engineered as a whole, preventing mix-and-match pitfalls that often cause leaks or premature wear. Over the lifecycle, these factors lower total cost of ownership by reducing rework, fluid losses, and downtime. For projects involving retrofits, a correctly specified REDUCING UNION within OEM parts allows staged upgrades while preserving system standards and safety margins.
Compliance for REDUCING UNION OEM parts in diesel and gas engines
Class-compliant materials, pressure ratings, and test certificates support audits and commissioning. Whether integrating a REDUCING UNION in a fuel return line or a sample line on a gas engine, conformity to relevant standards ensures interchangeability and predictable sealing behavior—key to safe operation at sea and in power plants.
MOPA – fast, secure supply of OEM parts for Fittings and armatures and REDUCING UNION
MOPA is an experienced partner for OEM spare parts suitable for fittings and armatures, including every major REDUCING UNION configuration. Customers rely on our speed, quality, and security in the trade of OEM parts for diesel and gas engines. We source to specification, provide clear documentation, and coordinate logistics that minimize vessel or plant downtime. Our technical team supports selection—thread form, sealing type, material, and pressure class—so your marine engine piping receives the exact parts it needs, first time.
Conclusion: Fittings and armatures with the right REDUCING UNION
Fittings and armatures are essential to safe, efficient engine operation, and the REDUCING UNION is a critical adapter that enables diameter transitions without compromising sealing or flow. Selecting OEM spare parts suitable for this category enhances performance, reliability, and service life while protecting maintenance budgets and operational uptime.