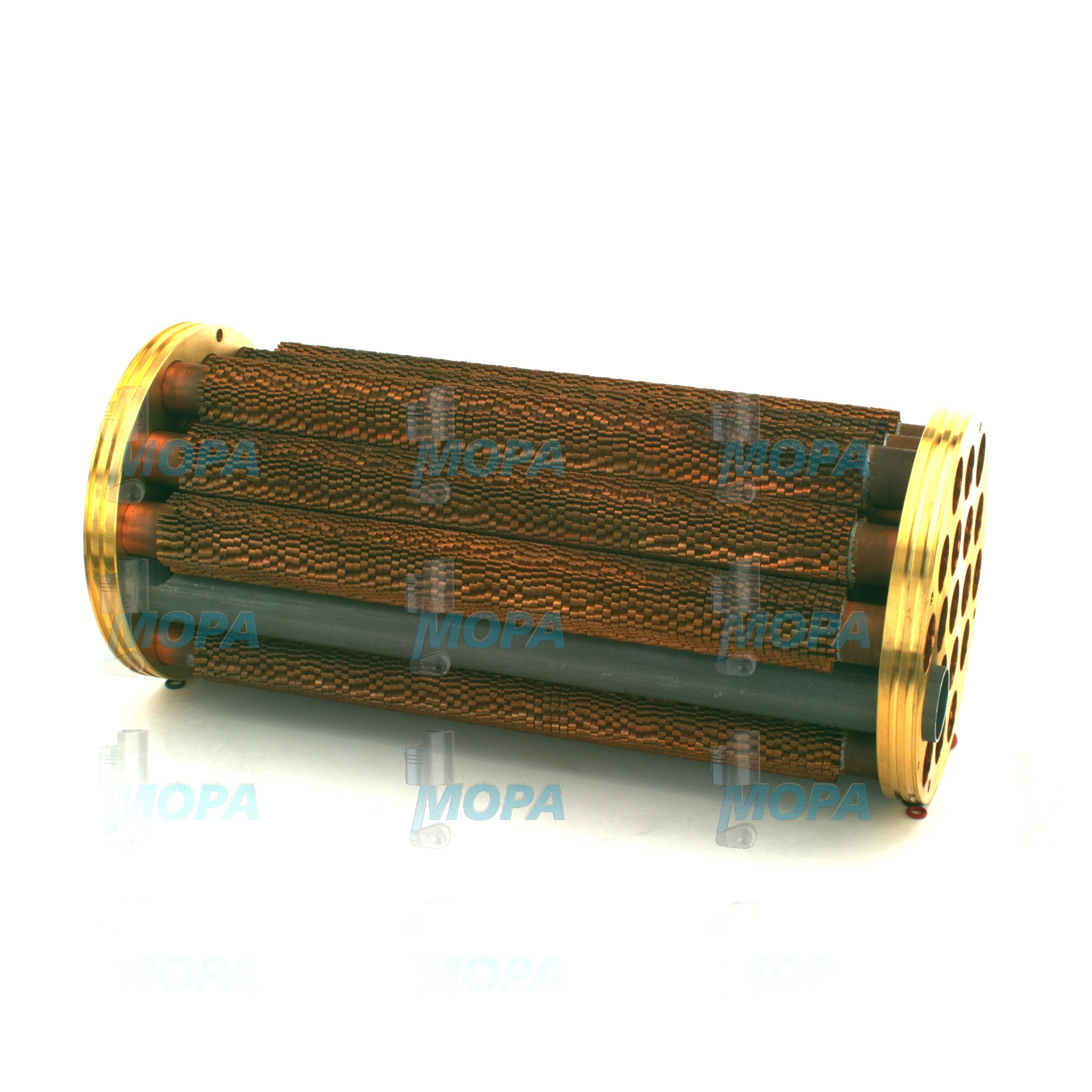
TUBE BUNDLE connections for Lines and Pipes in marine and diesel engines
Lines and pipes are the vascular system of any large marine engine or stationary diesel engine. They distribute fuel, lube oil, cooling water, charge air, hydraulics, and compressed air with controlled pressure and flow, linking pumps, filters, coolers, heat exchangers, and actuators. In many installations, they interface directly with a TUBE BUNDLE in coolers and heat exchangers to manage temperature, protect components, and stabilize performance under varying loads. Without robust, correctly specified lines and pipes, even the best engine hardware cannot deliver reliable power, safe operation, or efficient fuel burn.
This article category covers rigid pipes, formed tubing, and flexible hose assemblies along with their fittings, clamps, and seals. Materials range from carbon steel and precision seamless steel tubing to stainless steel (e.g., 316/316L), CuNi 90/10 for seawater service, and specialty alloys for high-temperature exhaust and EGR applications. Each choice is driven by medium, temperature, pressure class, and corrosion risk—factors that determine service life and maintenance cost across the engine’s lifecycle.
Technical function of lines and pipes with a TUBE BUNDLE in a marine engine
In a marine engine, lines and pipes form closed circuits that deliver media to and from components such as charge air coolers, jacket water coolers, lube oil coolers, and fuel conditioning skids. Where a cooler contains a TUBE BUNDLE (marine engine), the lines supply and return the medium through headers and channel covers, maintaining design flow (e.g., L/min or m³/h) and differential pressure to achieve required heat transfer. Proper routing minimizes pressure drop, avoids air pockets, and reduces vibration that can propagate to the tube sheet or cause fretting at supports.
Cooling-water lines in seawater applications typically use CuNi or coated steel, mitigating pitting and erosion-corrosion on inlet bends and reducers. Fuel lines are specified for pulsation and safety, often double-walled in machinery spaces, with leak detection to protect the engine and crew. Lube oil pipes must balance cleanliness and pressure stability to safeguard bearings, turbochargers, and valve gear. Charge air piping handles elevated temperatures and high flow velocities, connecting turbocharger outlets to coolers where the TUBE BUNDLE (diesel engine) reduces intake temperature for higher charge density and improved efficiency.
- · High-integrity flow paths for fuel, oil, water, and air
- · Material selection matched to medium, temperature, and pressure
- · Engineered bends and supports to reduce vibration and fatigue
- · Corrosion control for seawater and condensate exposure
- · Tightness and cleanliness to protect sensitive components
- · Correct diameters for flow, velocity, and pressure drop targets
- · Reliable interfaces to coolers with a TUBE BUNDLE and pump skids
Execution details matter: correct bending radii maintain wall thickness; double-ferrule or flare fittings per ISO standards secure joints under thermal cycling; and support spacing avoids resonance. Before commissioning, hydrostatic or pneumatic testing, followed by flushing to ISO cleanliness codes, prevents early failures in coolers and precision valves.
Importance for engine operation, reliability, and service life
Lines and pipes directly affect performance, emissions, and uptime. A minor restriction in cooling lines can raise charge air temperatures, reducing power density and accelerating turbocharger wear. Undersized or fouled lube oil pipes lead to pressure dips at bearings. Fuel line leaks introduce fire risk and unplanned off-hire. Vibration-induced cracks or loose supports can cause sudden coolant loss into a TUBE BUNDLE shell side, triggering high-temperature alarms and emergency shutdowns.
Typical risks when lines and pipes degrade
Corrosion (pitting, crevice, or MIC) in seawater circuits; erosion at elbows due to high velocity; fretting at supports; thermal expansion stresses near manifolds; seal hardening from heat; and contamination from inadequate flushing. Each failure mode raises lifecycle cost, complicates maintenance around heat exchangers, and can shorten the service interval of the tube bundle and connected equipment.
Advantages of OEM spare parts suitable for lines and pipes
Using OEM spare parts suitable for lines and pipes preserves the engineered flow characteristics and mechanical integrity designed for the engine platform. Dimensional fidelity, certified materials, and qualified joining methods reduce the risk of misalignment at cooler end covers and ensure leak-tight connections to a TUBE BUNDLE (OEM parts). For purchasers and shipowners, this translates into predictable maintenance windows, stable performance, and clear documentation traceability.
Performance: Correct wall thickness, surface finish, and bend geometry keep pressure drop within specification, protecting pump margins and heat exchanger duty.
Reliability: Proven materials and coatings resist corrosion and thermal cycling, extending MTBF for circuits connected to lube, fuel, and cooling systems.
Budget: Longer service intervals, less rework during docking, and fewer unplanned stoppages lower total cost of ownership.
Service life: Proper metallurgy and certified fabrication help the engine, including components interacting with the tube bundle, reach design life without premature replacement.
MOPA as your partner for OEM spare parts lines and pipes
MOPA supplies OEM spare parts for lines and pipes—and the related interfaces to coolers and heat exchangers—across leading diesel and gas engine platforms. Customers rely on fast response, consistent quality, and secure sourcing for time-critical jobs, whether replacing seawater inlet spools, fuel return manifolds, charge air elbows, or connectors to a TUBE BUNDLE (marine engine).
Our team supports specification checks, cross-references, and delivery scheduling to keep downtime minimal. With rigorous documentation and part traceability, MOPA streamlines procurement for shipyards, fleet operators, and power plant owners who demand predictable lead times and dependable performance from their engine piping systems.
Conclusion: Lines and pipes with TUBE BUNDLE interfaces
Lines and pipes are foundational to engine performance, tying pumps, filters, and coolers to the TUBE BUNDLE that controls temperature and efficiency. Selecting and maintaining the right components safeguards reliability, safety, and lifecycle cost.
Partnering with MOPA for OEM spare parts suitable for lines and pipes ensures the precision, speed, and security needed to keep marine and diesel engines running at their designed potential.