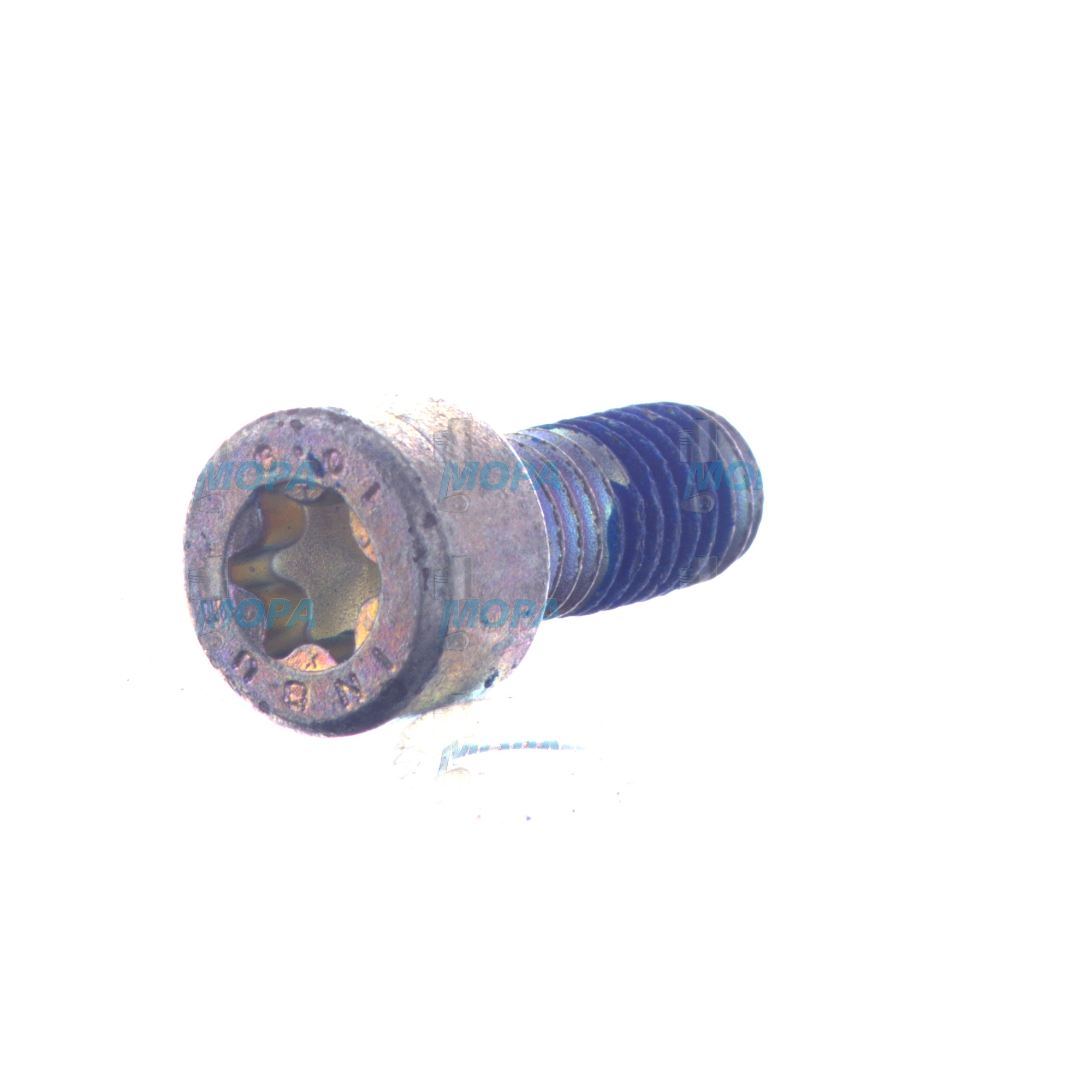
SOCKET-HEAD SCREW – Screws for Marine and Diesel Engines
Screws are precision fasteners that hold engine assemblies together under high thermal and mechanical loads. In a marine engine room or power plant, their job is simple yet critical: create reliable clamping force that keeps housings sealed, components aligned, and vibration under control. Among these, the SOCKET-HEAD SCREW stands out for compact head geometry, high torque transfer, and safe installation in confined spaces—key benefits when working around pumps, turbochargers, manifolds, and auxiliary equipment. Selecting the right screws and keeping them in top condition directly affects performance, safety, and service life of diesel and gas engines.
Technical function of screws and the SOCKET-HEAD SCREW in engine applications
In engines, screws convert tightening torque into axial preload. This preload clamps mating parts—such as covers, gear cases, instrumentation brackets, and turbocharger interfaces—so they resist shear forces and cyclic vibration. The SOCKET-HEAD SCREW marine engine technicians prefer uses an internal hex drive that enables high tightening forces even where tool access is limited. On a diesel engine, socket-head cap screws (ISO 4762 / DIN 912) are often specified for precision-mounted components like sensor brackets, fuel equipment holders, and timing covers, where accurate preload and compact head geometry are vital.
Key to the function is consistency: material strength class (e.g., 10.9 or 12.9 alloy steel), controlled heat treatment, and surface finish determine how a screw stretches elastically to produce clamping force. Proper friction coefficients—achieved via phosphate, zinc-flake, or molybdenum-coated finishes—ensure that applied torque translates into predictable preload rather than being lost to thread and under-head friction. In high-temperature zones, stainless or high-alloy screws must maintain strength and resist creep. Where corrosion from salt spray or condensate is a risk, A4 stainless or coated alloy steel fasteners prevent thread seizure and maintain removal torque across service intervals. For tight assemblies, the SOCKET-HEAD SCREW diesel engine builders select allows direct access with a hex key or bit, reducing risk of cam-out and head damage.
Load cases, preload control, and safety
Engines impose dynamic loads—torsional vibration, thermal cycling, and pulsating pressures. Correctly specified screws counter these by maintaining preload through the full duty cycle. Techniques such as torque-angle tightening, use of liquid threadlocker, spring or wedge-lock washers, and adherence to clean-lubed assembly practices help prevent self-loosening. Where alignment is critical (e.g., instrument rails or pump flanges), socket-head designs provide uniform head support and precise seating. For sensitive interfaces, metric fine threads or UNF can increase axial resolution and vibration resistance.
Key characteristics and advantages of screws in engines
· High tensile strength classes (8.8 / 10.9 / 12.9) for reliable preload.
· Standards-compliant designs (ISO 4762 / DIN 912; ISO 898-1 mechanical properties).
· Drive types for tight spaces: SOCKET-HEAD SCREW with internal hex or Torx.
· Materials for environment: alloy steel, A2/A4 stainless, high-temp alloys.
· Protective finishes: phosphate, zinc-flake, nickel, or moly-coated surfaces.
· Thread forms: metric coarse/fine, UNC/UNF for global service compatibility.
· Corrosion and vibration resistance for marine and power-generation duty.
· Predictable friction coefficients for accurate torque-preload conversion.
Why screws are critical for reliability and service life
Every engine relies on stable clamping to protect sealing faces, bearing alignments, and rotating equipment interfaces. If screws wear, corrode, or stretch beyond elastic limits, preload drops. The result can be oil or coolant leaks, flange fretting, shaft misalignment, increased vibration, and ultimately fatigue cracks or component loss. Damaged recesses on a SOCKET-HEAD SCREW marine engine fitting can impede proper torque application, encouraging under-tightening and progressive loosening. Thread galling or pitting in humid and salty atmospheres can lock fasteners in place, causing costly removal and unexpected downtime. Routine inspection for head rounding, thread damage, corrosion, and signs of embedment is essential, and critical screws should be replaced during overhauls according to engine-maker intervals.
Advantages of OEM spare parts suitable for screws
For high-output diesel and gas engines, using OEM spare parts suitable for screws safeguards the exact materials, tolerances, and surface finishes that the design requires. Consistency of steel grade, heat treatment, and coating is vital to repeatable preload and long-term stability. The SOCKET-HEAD SCREW OEM parts route provides dimensional accuracy (head height, bearing face flatness, concentricity), controlled friction coefficients, and batch traceability that supports safe operations and transparent maintenance records. This precision reduces rework, limits the risk of mixed-strength fasteners in critical joints, and supports predictable torque-angle tightening strategies across fleets.
Beyond performance, OEM spare parts suitable for screws help protect your maintenance budget. Accurate fit saves installation time, lowers the chance of thread repair, and reduces unplanned stops. In corrosive, high-vibration environments, correct coatings and compatible materials extend service intervals and preserve mating components, protecting the overall engine asset. Whether it is a cover clamp or a high-strength SOCKET-HEAD SCREW diesel engine application, like turbocharger brackets, the right fastener specification keeps performance stable, emissions in check, and safety margins intact.
MOPA – your partner for OEM spare parts screws
MOPA is an experienced and reliable partner for OEM spare parts screws across diesel and gas engines. We source and supply SOCKET-HEAD SCREW OEM parts with speed, quality, and security—supporting tight docking schedules and planned outages. Our team ensures the correct standards (ISO/DIN), strength classes, and finishes for each engine type, and can align deliveries with overhaul kits and fleet-specific BOMs. With responsive logistics, documentation on request (e.g., material certificates), and a focus on marine and power-generation requirements, MOPA helps purchasers, shipowners, and technical managers keep engines running safely and efficiently.
Conclusion: SOCKET-HEAD SCREW screws at a glance
Screws—especially the compact and robust SOCKET-HEAD SCREW—are fundamental to engine integrity, delivering the clamping force that holds systems together under heat, vibration, and load. OEM spare parts suitable for screws provide the precision, material consistency, and corrosion protection needed for sustained performance, reliability, and lifecycle value. Choose the right specification and partner with MOPA to keep your diesel and gas engines secure and productive.